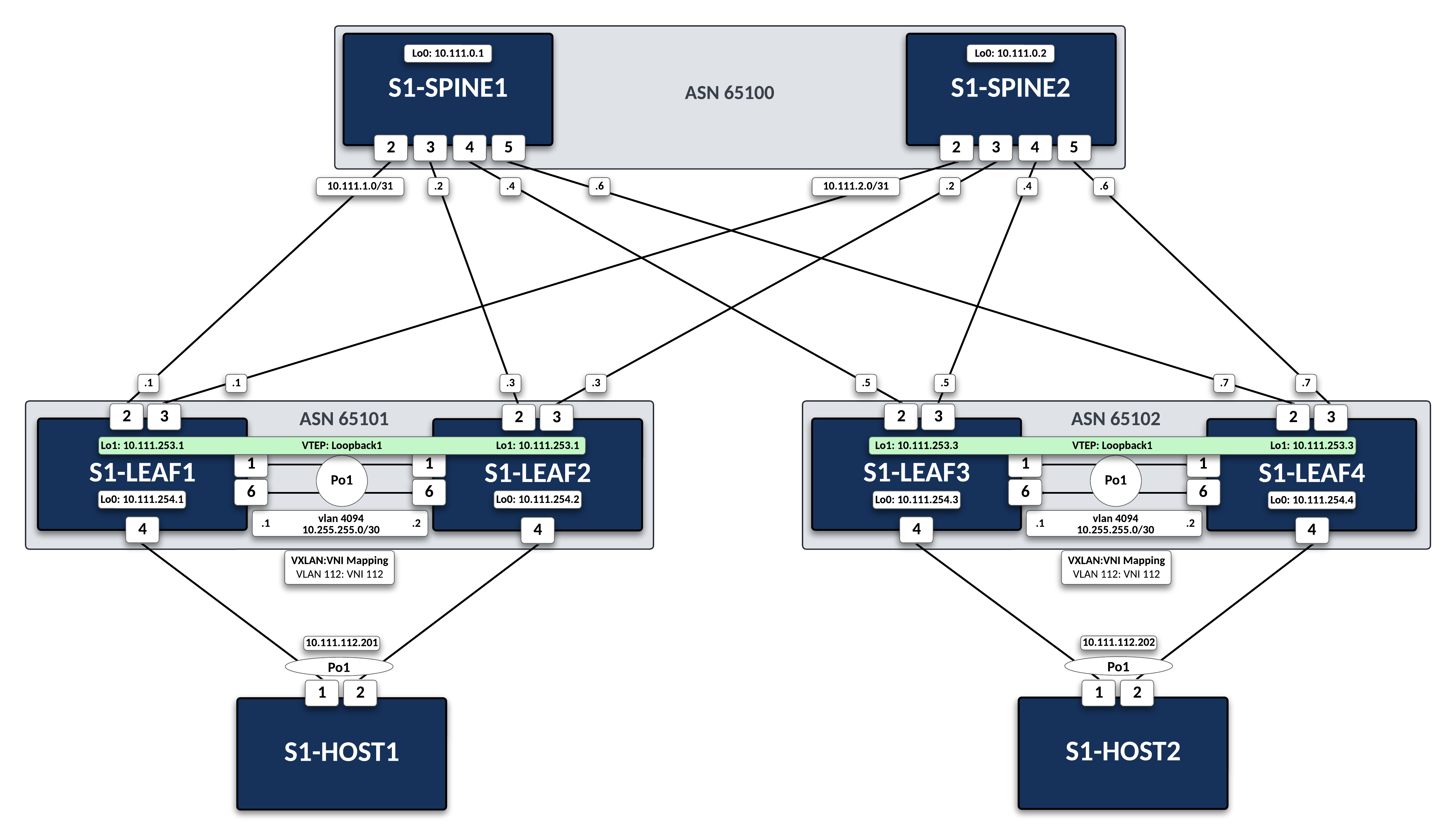
VXLAN Lab¶
Note
The manually entered commands that are part of this lab are equivalent to VXLAN_s1-leaf4_complete.
Preparing The Lab¶
-
Log into the LabAccess jumpserver:
-
Type
vxlanat the Main Menu prompt.Info
Did you know the VXLAN script is composed of Python code that uses the CloudVision Portal REST API to automate the provisioning of CVP Configlets? The configlets that are configured via the REST API are
VXLAN_s1-spine1,VXLAN_s1-spine2,VXLAN_s1-leaf1,VXLAN_s1-leaf2,VXLAN_s1-leaf3, andVXLAN_s1-leaf4. In addition each leaf also gets theVLANsconfiglet. -
The script will pre-configure the topology with the exception of s1-Leaf4. The main task is to configure this device.
-
Lab Tasks¶
-
On
s1-leaf4, configure Port-channels connecting tos1-host2:Commands
-
Verify MLAG on
s1-leaf4.Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config)#show mlag MLAG Configuration: domain-id : MLAG local-interface : Vlan4094 peer-address : 10.255.255.1 peer-link : Port-Channel1 peer-config : inconsistent MLAG Status: state : Active negotiation status : Connected peer-link status : Up local-int status : Up system-id : 02:1c:73:c0:c6:14 dual-primary detection : Disabled dual-primary interface errdisabled : False MLAG Ports: Disabled : 0 Configured : 0 Inactive : 0 Active-partial : 0 Active-full : 1Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config)#show mlag interfaces local/remote mlag desc state local remote status ---------- ---------- ----------------- ----------- ------------ ------------ 5 MLAG - HOST2 active-full Po5 Po5 up/upCommand
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config)#show port-channel dense Flags -------------------------- ----------------------------- ------------------------- a - LACP Active p - LACP Passive * - static fallback F - Fallback enabled f - Fallback configured ^ - individual fallback U - In Use D - Down + - In-Sync - - Out-of-Sync i - incompatible with agg P - bundled in Po s - suspended G - Aggregable I - Individual S - ShortTimeout w - wait for agg E - Inactive. The number of configured port channels exceeds the config limit M - Exceeds maximum weight Number of channels in use: 2 Number of aggregators: 2 Port-Channel Protocol Ports ------------------ -------------- ------------------ Po1(U) LACP(a) Et1(PG+) Et6(PG+) Po5(U) LACP(a) Et4(PSG+) PEt4(P) -
Validate BGP operation on
s1-leaf4.Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config)#sh run sec bgp router bgp 65102 router-id 10.111.254.4 maximum-paths 2 neighbor SPINE peer group neighbor SPINE remote-as 65100 neighbor SPINE send-community standard extended neighbor 10.111.1.6 peer group SPINE neighbor 10.111.2.6 peer group SPINE neighbor 10.255.255.1 remote-as 65102 neighbor 10.255.255.1 next-hop-self network 10.111.112.0/24 network 10.111.134.0/24 network 10.111.254.4/32Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config)#show ip route bgp VRF: default Codes: C - connected, S - static, K - kernel, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area, E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type2, B - Other BGP Routes, B I - iBGP, B E - eBGP, R - RIP, I L1 - IS-IS level 1, I L2 - IS-IS level 2, O3 - OSPFv3, A B - BGP Aggregate, A O - OSPF Summary, NG - Nexthop Group Static Route, V - VXLAN Control Service, M - Martian, DH - DHCP client installed default route, DP - Dynamic Policy Route, L - VRF Leaked, G - gRIBI, RC - Route Cache Route B E 10.111.0.1/32 [200/0] via 10.111.1.6, Ethernet2 B E 10.111.0.2/32 [200/0] via 10.111.2.6, Ethernet3 B E 10.111.1.0/24 [200/0] via 10.111.1.6, Ethernet2 B E 10.111.2.0/24 [200/0] via 10.111.2.6, Ethernet3 B E 10.111.253.1/32 [200/0] via 10.111.1.6, Ethernet2 via 10.111.2.6, Ethernet3 B I 10.111.253.3/32 [200/0] via 10.255.255.1, Vlan4094 B E 10.111.254.1/32 [200/0] via 10.111.1.6, Ethernet2 via 10.111.2.6, Ethernet3 B E 10.111.254.2/32 [200/0] via 10.111.1.6, Ethernet2 via 10.111.2.6, Ethernet3 B I 10.111.254.3/32 [200/0] via 10.255.255.1, Vlan4094Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config)#show ip interface brief Address Interface IP Address Status Protocol MTU Owner ----------------- --------------------- ------------ -------------- ----------- ------- Ethernet2 10.111.1.7/31 up up 1500 Ethernet3 10.111.2.7/31 up up 1500 Loopback0 10.111.254.4/32 up up 65535 Management0 192.168.0.15/24 up up 1500 Vlan112 10.111.112.1/24 up up 1500 Vlan134 10.111.134.1/24 up up 1500 Vlan4094 10.255.255.2/30 up up 1500Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config)#show ip bgp summary BGP summary information for VRF default Router identifier 10.111.254.4, local AS number 65102 Neighbor Status Codes: m - Under maintenance Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent InQ OutQ Up/Down State PfxRcd PfxAcc 10.111.1.6 4 65100 333 335 0 0 04:34:48 Estab 5 5 10.111.2.6 4 65100 329 332 0 0 04:34:58 Estab 6 6 10.255.255.1 4 65102 335 333 0 0 04:34:46 Estab 11 11BGP Notes
show ip bgp summarywill show that the BGP neighbors have moved to Estab state. Note the iBGP peering betweenLeaf3&Leaf4. Also note the route to the shared loopback1 ofLeaf1&Leaf2. This is the remote VTEP on the other side of the spine-leaf network. -
Create Loopback1 and the VXLAN VTEP (VTI) interfaces on
s1-leaf4.Commands
configure interface Loopback1 ip address 10.111.253.3/32 interface vxlan 1 vxlan source-interface loopback 1 vxlan vlan 112 vni 112 vxlan flood vtep 10.111.253.1Note
vxlan flood vtep 10.111.253.1 adds the shared loopback1 IP address on
Leaf1&Leaf2to the HER list. Note that for autodiscovery of VTEPs, one must use BGP eVPN (see eVPN labs) or CVX.Verification
Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config)#show run int vxlan1 interface Vxlan1 vxlan source-interface Loopback1 vxlan udp-port 4789 vxlan vlan 112 vni 112 vxlan flood vtep 10.111.253.1Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config-if-Vx1)#sh int vxlan 1 Vxlan1 is up, line protocol is up (connected) Hardware is Vxlan Source interface is Loopback1 and is active with 10.111.253.3 Replication/Flood Mode is headend with Flood List Source: CLI Remote MAC learning via Datapath VNI mapping to VLANs Static VLAN to VNI mapping is [12, 112] Note: All Dynamic VLANs used by VCS are internal VLANs. Use 'show vxlan vni' for details. Static VRF to VNI mapping is not configured Headend replication flood vtep list is: 12 10.111.253.1 MLAG Shared Router MAC is 0000.0000.0000 -
Log into
s1-host1ands1-host2and ping the vARP VIP and the other host.Commands From s1-host1
Note
Note the TTL in the ping outputs above. Even though .202 is many switches away, it appears locally connected and has the same TTL as the ping to .1. It’s also interesting to realize that due to MLAG hashing of both the ARP requests and ping packet flows that pings to the SVI addresses of .2 & .3 may or may not work. Do you know why?
Verify MAC/ARP tables on
s1-host1:Command
Expected Output
Command
Expected Output
s1-host1#show arp Address Age (sec) Hardware Addr Interface 192.168.0.1 0:00:00 124e.b1e1.7180 Management0 192.168.0.5 0:00:05 001c.73a0.c601 Management0 10.111.112.1 0:38:05 001c.7300.0001 Port-Channel1 10.111.112.202 0:14:05 001c.73c0.c617 Port-Channel1Commands *From s1-host12
Note
Note the TTL in the ping outputs above. Even though .201 is many switches away, it appears locally connected and has the same TTL as the ping to .1. Also note that the vARP VIP (10.111.112.1) address & and vARP MAC address (00:1c:73:00:00:ff) are the same for both leaf pairs - this IP address is known as an AnyCast IP address. If a VM was motioning from
s1-host1tos1-host2for maintenance, the default GW address nor the ARP cache on that VM need to change.Verify MAC/ARP tables on
s1-host2:Commands
Note
Note the MAC addresses returned by the commands above and compare to the prior grep and arp commands and see that both hosts appear to each other as though they are on the same L2 broadcast domain. For a little extra fun, as you are running the pings from
host1, on another set of windows fors1-leaf1ands1-leaf2, issue clear counters then issue watch 1 diff show int e4 counter and see how MLAG hashing across the different pings causes the packets to choose a particular member of the port-channel in both the outbound & inbound ping flows.
Test¶
Perform the following verification steps on s1-leaf1 and s1-leaf4.
-
Verify the MAC addresses and the associated VXLAN VTEP.
Command s1-leaf1
Expected Output
s1-leaf1#show vxlan vtep Remote VTEPS for Vxlan1: VTEP Tunnel Type(s) ------------------ -------------- 10.111.253.3 unicast, flood Total number of remote VTEPS: 1Command s1-leaf1
Expected Output
s1-leaf1#show vxlan address-table Vxlan Mac Address Table ---------------------------------------------------------------------- VLAN Mac Address Type Prt VTEP Moves Last Move ---- ----------- ---- --- ---- ----- --------- 112 001c.73c0.c617 DYNAMIC Vx1 10.111.253.3 1 0:01:13 ago Total Remote Mac Addresses for this criterion: 1Command s1-leaf4
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config)#show vxlan vtep Remote VTEPS for Vxlan1: VTEP Tunnel Type(s) ------------------ -------------- 10.111.253.1 unicast, flood Total number of remote VTEPS: 1Command s1-leaf4
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config)#show vxlan address-table Vxlan Mac Address Table ---------------------------------------------------------------------- VLAN Mac Address Type Prt VTEP Moves Last Move ---- ----------- ---- --- ---- ----- --------- 112 001c.73c0.c616 DYNAMIC Vx1 10.111.253.1 1 0:00:33 ago Total Remote Mac Addresses for this criterion: 1Note
For show vxlan vtep and show vxlan address-table to be populated, the above pings need to have been active very recently so that the MAC addresses don’t age out, and you’ll notice that at least 1 (but not necessarily both) of the MLAG pair switches (
s1-leaf1ors1-leaf2) will have knowledge of the remote VTEP. This is because this is the direction the pings (inbound & outbound) last hashed. -
Verify the MAC addresses and the associated interfaces.
Command
Success
If your VXLAN output looked similar to the above, and you had reachability between s1-host1 and s1-host2, then your lab was successful.
Tip
We can run some other show commands and tests to verify VXLAN. On s1-leaf1 and s1-leaf4, issue the following commands:
- show interface vxlan1
- show mac address-table
- show log