Media STP and SVI Lab¶
History
The Spanning-Tree protocol (STP) was initially invented in 1985 and is one of the oldest networking protocols being used in Layer 2 network topologies today. STP is classified as a network protocol that builds loop-free logical topology for Ethernet (initially bridged) networks.
Info
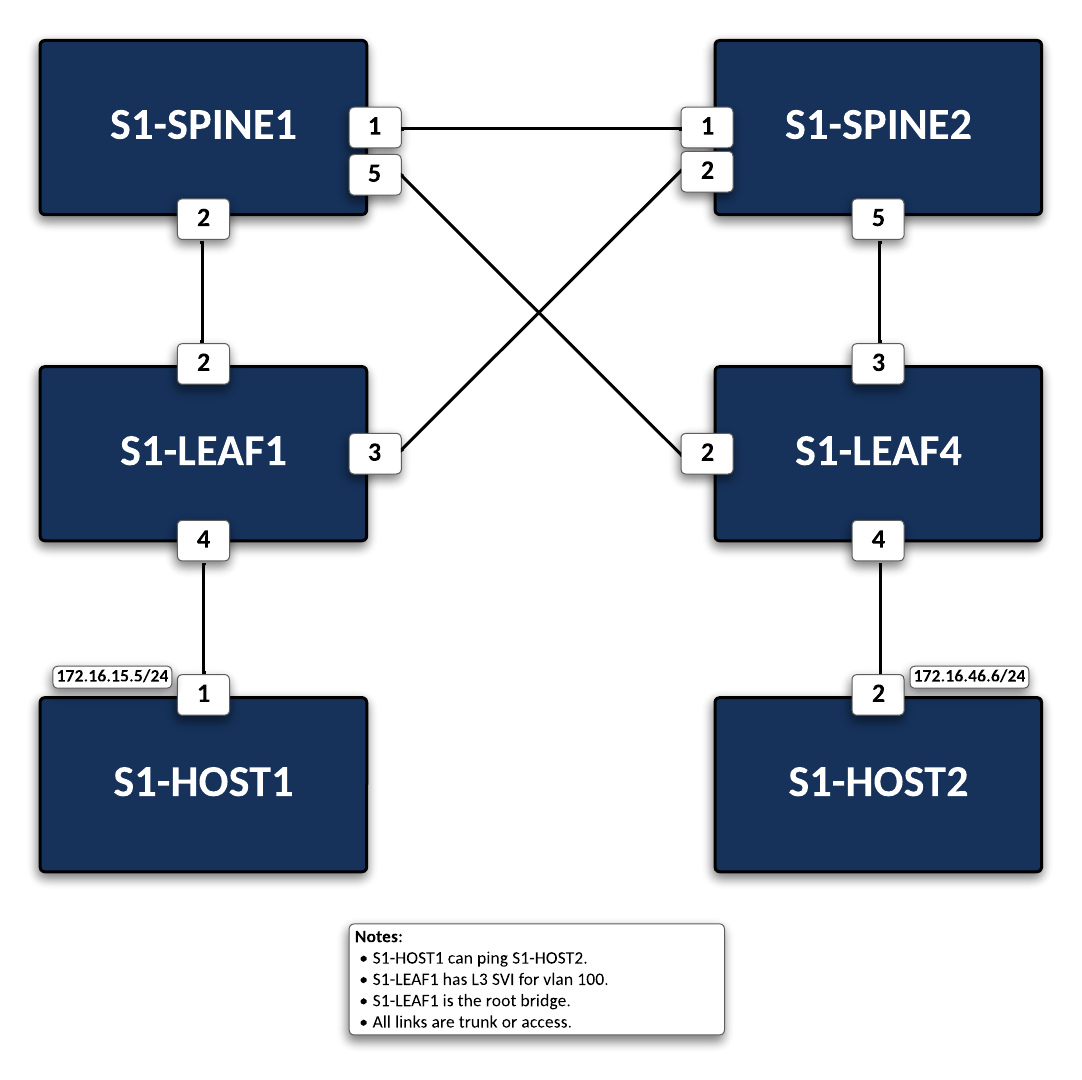
This lab has been limited to the following devices: s1-Spine1, s1-Spine2, s1-Leaf1, s1-Leaf4, s1-Host1, and s1-Host2. Additional devices on this topology are out of scope for this lab.
Preparing The Lab¶
- Log into the LabAccess jumpserver:
- Type
labsat the Main Menu prompt. This will bring up additional lab menu selections. - Type
media-labsat this prompt to open the media lab section. - Type
media-vlanat this prompt and wait for the process to run. - The script will configure the topology with the exception of s1-Leaf4. The main task is to configure this device so there is connectivity between the two hosts.
- Type
Verification¶
On s1-Spine2, verify spanning-tree operation in the topology. You should see s1-Spine1 as the root bridge by viewing the Bridge ID and the interfaces designated as a Root port. Root ports points towards the root bridge, which in this case would be s1-Spine1.
When you run the following command which interfaces would you expect to be your root ports?
Expected Output
s1-spine2#show spanning-tree
MST0
Spanning tree enabled protocol mstp
Root ID Priority 4096
Address 2cc2.6056.df93
Cost 0 (Ext) 2000 (Int)
Port 1 (Ethernet1)
Hello Time 2.000 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 8192 (priority 8192 sys-id-ext 0)
Address 2cc2.6094.d76c
Hello Time 2.000 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Interface Role State Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---------- ---------- --------- -------- --------------------
Et1 root forwarding 2000 128.1 P2p
Et2 designated forwarding 2000 128.2 P2p
Et5 designated forwarding 2000 128.5 P2p
Et6 designated forwarding 2000 128.6 P2p Edge
Et7 designated forwarding 2000 128.7 P2p Edge
Lab Tasks¶
Configure VLANs and Interfaces¶
Configure the VLAN and interface types on s1-Leaf4 to allow spanning-tree protocol to operate and have reachability to s1-Host2.
-
On
s1-Leaf4, create the Layer 2 instance of vlan 100. Creating this vlan will add it to the spanning-tree process:Example
We can verify its creation with the following command, which will also show if there are any physical interfaces associated with the vlan:
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config-vlan-100)#show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports ----- -------------------------------- --------- ------------------------------- 1 default active Et2, Et3, Et4, Et6, Et7, Et8 Et9, Et10, Et11, Et12, Et13 Et14, Et15, Et16, Et17, Et18 Et19, Et20, Et21, Et22, Et23 Et24, Et25, Et26, Et27, Et28 Et29, Et30, Et31, Et32 12 VLAN0012 active 34 VLAN0034 active 100 v100 active -
Once the vlan is created, we can define the following uplink ports on s1-Leaf4 as trunks, as well as allow vlan 100 on the trunk:
configure interface Ethernet2 switchport trunk allowed vlan 100 switchport mode trunk ! interface Ethernet3 switchport trunk allowed vlan 100 switchport mode trunk !Example
s1-leaf4(config-vlan-100)#configure s1-leaf4(config)#interface ethernet 2-3 s1-leaf4(config-if-Et2-3)#switchport mode trunk s1-leaf4(config-if-Et2-3)#switchport trunk allowed vlan 100Info
By default, once an interface is configured as a trunk, all vlans will be associated to it.
Once the interface configuration has been completed for the trunk links, you can verify the spanning-tree topology and see the root bridge is
s1-Spine1and the connection tos1-Spine2has been blocked for loop prevention:Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et2-3)#show spanning-tree MST0 Spanning tree enabled protocol mstp Root ID Priority 4096 Address 2cc2.6056.df93 Cost 0 (Ext) 2000 (Int) Port 2 (Ethernet2) Hello Time 2.000 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 32768 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 0) Address 2cc2.60b5.96d9 Hello Time 2.000 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Interface Role State Cost Prio.Nbr Type ---------------- ---------- ---------- --------- -------- -------------------- Et2 root forwarding 2000 128.2 P2p Et3 alternate discarding 2000 128.3 P2p Et4 designated forwarding 2000 128.4 P2p Edge Et6 designated forwarding 2000 128.6 P2p Edge Et7 designated forwarding 2000 128.7 P2p Edge Et8 designated forwarding 2000 128.8 P2p Edge Et9 designated forwarding 2000 128.9 P2p Edge Et10 designated forwarding 2000 128.10 P2p Edge -
Once the Layer 2 topology has been setup, we can configure the port towards our host as an access port to allow s1-Host2 to pass traffic into the network:
Example
Test¶
Validate end-to-end connectivity after configuring the Layer 2 interfaces. Once spanning-tree has converged for the topology we can observe the results.
-
You should see the root bridge is towards
s1-Spine1and vlan 100 should be associated to interfaces eth2, eth3, and eth4. Validate the vlan port association and spanning-tree topology is correct with the following commands:Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et4)#show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports ----- -------------------------------- --------- ------------------------------- 1 default active Et6, Et7, Et8, Et9, Et10, Et11 Et12, Et13, Et14, Et15, Et16 Et17, Et18, Et19, Et20, Et21 Et22, Et23, Et24, Et25, Et26 Et27, Et28, Et29, Et30, Et31 Et32 12 VLAN0012 active 34 VLAN0034 active 100 v100 active Et2, Et3, Et4Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et3)#show spanning-tree MST0 Spanning tree enabled protocol mstp Root ID Priority 4096 Address 2cc2.6056.df93 Cost 0 (Ext) 2000 (Int) Port 2 (Ethernet2) Hello Time 2.000 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 32768 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 0) Address 2cc2.60b5.96d9 Hello Time 2.000 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Interface Role State Cost Prio.Nbr Type ---------------- ---------- ---------- --------- -------- -------------------- Et2 root forwarding 2000 128.2 P2p Et3 alternate discarding 2000 128.3 P2p Et4 designated forwarding 2000 128.4 P2p Edge Et6 designated forwarding 2000 128.6 P2p Edge Et7 designated forwarding 2000 128.7 P2p Edge Et8 designated forwarding 2000 128.8 P2p Edge Et9 designated forwarding 2000 128.9 P2p Edge Et10 designated forwarding 2000 128.10 P2p Edge -
Log into
s1-Host2and verify you can reach the SVI for vlan 100:.Expected Output
s1-host2# ping 172.16.46.4 PING 172.16.46.4 (172.16.46.4) 72(100) bytes of data. 80 bytes from 172.16.46.4: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=35.3 ms 80 bytes from 172.16.46.4: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=51.3 ms 80 bytes from 172.16.46.4: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=49.9 ms 80 bytes from 172.16.46.4: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=48.9 ms 80 bytes from 172.16.46.4: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=35.6 ms --- 172.16.46.4 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 received, 0% packet loss, time 73ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 35.313/44.256/51.377/7.192 ms, pipe 4, ipg/ewma 18.302/39.598 ms -
Verify reachability to
s1-Host1Expected Output
s1-host2# ping 172.16.15.5 PING 172.16.15.5 (172.16.15.5) 72(100) bytes of data. From 172.16.46.4: icmp_seq=1 Redirect Host(New nexthop: 172.16.15.5) 80 bytes from 172.16.15.5: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=237 ms 80 bytes from 172.16.15.5: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=233 ms 80 bytes from 172.16.15.5: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=250 ms 80 bytes from 172.16.15.5: icmp_seq=4 ttl=63 time=257 ms 80 bytes from 172.16.15.5: icmp_seq=5 ttl=63 time=257 ms --- 172.16.15.5 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 received, 0% packet loss, time 43ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 233.030/247.345/257.699/10.206 ms, pipe 5, ipg/ewma 10.926/243.255 ms
Success
If all the SVI and STP settings have been completed correctly you should be able to ping the remote host as well as the SVI interface itself configured on s1-Spine1 which is also the root bridge for this topology!
Test your knowledge
When you are verifying the spanning-tree topology from s1-Leaf4, what are some of the reasons for the root bridge selection?
Tip
The following additional commands are useful to verify connectivity for validation and troubleshooting purposes:
- show vlan
- show interfaces trunk
- show interfaces status
- show spanning-tree