Media Intro to IP Lab¶
Info
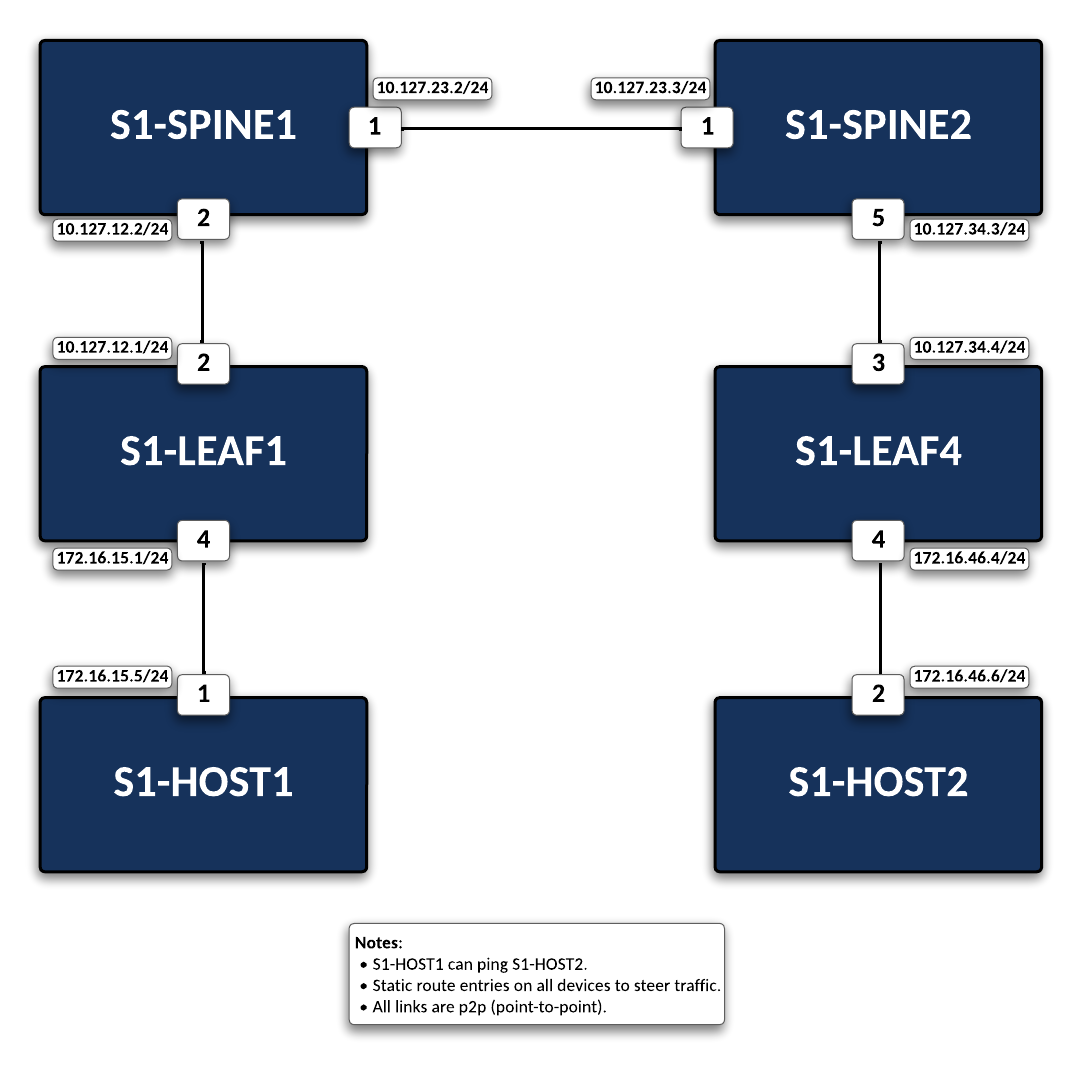
This lab has been limited to the following devices: s1-Spine1, s1-Spine2, s1-Leaf1, s1-Leaf4, s1-Host1, and s1-Host2. Additional devices on this topology are out of scope for this lab.
Preparing The Lab¶
-
Log into the LabAccess jumpserver:
- Type
labsat the Main Menu prompt. This will bring up additional lab menu selections. - Type
media-labsat this prompt to open the media lab section. - Type
media-introat this prompt and wait for the process to run. - The script will configure the topology with the exception of s1-Leaf4. The main task is to configure this device so there is connectivity between the two hosts.
- Type
-
Connect to s1-Leaf4 from the menu:
- Connect to s1-Leaf4 by either selecting option 10 from the Device SSH menu (Type ssh at the prompt), or returning to the main ATD Topology screen and clicking on s1-Leaf4 on the network diagram.
- Once in the switch we are in the Privileged EXEC mode, denoted by the # preceding the device name. This is similar to an admin user and in this mode one can configure and view information on the switch. To configure devices, we will need to enter global configuration mode by typing
configureat the prompt, which will bring you into Privileged EXEC (enable) mode. - As you complete the labs you will see this configure command being used to ensure that you are in config mode. One prompt that you may come across is
>which denotes that you are in EXEC mode. In this mode you can perform basic tests and view system information. EXEC mode is the default mode for all switches.
Lab Tasks¶
Note
An IP address serves two principal functions. It identifies the host, or more specifically its network interface, and it provides the location of the host in the network, and thus the capability of establishing a path to that host. Its role has been characterized as follows: “A name indicates what we seek. An address indicates where it is. A route indicates how to get there.”
Configure IP Addressing¶
Configure the proper IP address on the respective interfaces along with the appropriate static routes to ensure there is end-to-end connectivity for the two end hosts to reach each other. All interfaces in this lab are designed as point-to-point connections.
On s1-Leaf4 assign the appropriate IP address and ensure the adjacent devices can be reached:
configure
!
interface Ethernet 3
no switchport
ip address 10.127.34.4/24
!
interface Ethernet 4
no switchport
ip address 172.16.46.4/24
Example
s1-leaf4#configure
s1-leaf4(config)#interface ethernet 3
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et3)#no switchport
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et3)#ip address 10.127.34.4/24
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et3)#interface ethernet 4
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et4)#no switchport
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et4)#ip address 172.16.46.4/24
Note
By default, all interfaces on an Arista switch are configured as a Layer 2 switchport. In order to configure the port as a Layer 3 routed port, the no switchport command is entered.
Test¶
Once the IP addresses have been added to the appropriate interfaces, ensure reachability to the adjacent device by leveraging the ping command from s1-Leaf4 as follows:
Commands
Expected Output
s1-leaf4# ping 10.127.34.3
PING 10.127.34.3 (10.127.34.3) 72(100) bytes of data.
80 bytes from 10.127.34.3: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=17.0 ms
80 bytes from 10.127.34.3: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=18.8 ms
80 bytes from 10.127.34.3: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=14.9 ms
80 bytes from 10.127.34.3: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=12.6 ms
--- 10.127.34.3 ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 4 received, 20% packet loss, time 62ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 12.605/15.868/18.844/2.332 ms, pipe 2, ipg/ewma 15.602/16.435 ms
s1-leaf4# ping 172.16.46.6
PING 172.16.46.6 (172.16.46.6) 72(100) bytes of data.
80 bytes from 172.16.46.6: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=38.4 ms
80 bytes from 172.16.46.6: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=32.1 ms
80 bytes from 172.16.46.6: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=28.0 ms
80 bytes from 172.16.46.6: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=31.6 ms
80 bytes from 172.16.46.6: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=12.7 ms
--- 172.16.46.6 ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 5 received, 0% packet loss, time 68ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 12.797/28.603/38.419/8.584 ms, pipe 4, ipg/ewma 17.163/32.954 ms
Success
At this point if the adjacent devices can be reached, you have configured the IP address correctly!
Configure Routing¶
Once the IP addresses have been assigned to the appropriate interfaces, we can enable routing, as well as add the appropriate static routes on s1-Leaf4 to allow reachability between the two host end-points as follows:
Example
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et4)#configure
s1-leaf4(config)#ip routing
s1-leaf4(config)#ip route 172.16.15.0/24 10.127.34.3
Note
We added the entire prefix for the static route, but we could have also put the specific host address. Normally your use case will dictate which approach to take.
Verification¶
Validate end-to-end connectivity from the s1-Host2 to s1-Host1 as follows:
Expected Output
s1-host2# ping 172.16.15.5
PING 172.16.15.5 (172.16.15.5) 72(100) bytes of data.
80 bytes from 172.16.15.5: icmp_seq=1 ttl=60 time=307 ms
80 bytes from 172.16.15.5: icmp_seq=2 ttl=60 time=300 ms
80 bytes from 172.16.15.5: icmp_seq=3 ttl=60 time=296 ms
80 bytes from 172.16.15.5: icmp_seq=4 ttl=60 time=293 ms
80 bytes from 172.16.15.5: icmp_seq=5 ttl=60 time=289 ms
--- 172.16.15.5 ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 5 received, 0% packet loss, time 43ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 289.129/297.583/307.932/6.497 ms, pipe 5, ipg/ewma 10.984/302.312 ms
Success
If all the IP address and routing settings have been completed correctly, then you should have reachability!
Test your knowledge
When s1-Leaf4 receives an incoming icmp packet from s1-Host2, what would the process be for the switch to determine the path for the packet to be forwarded?
Tip
The following additional commands are useful to verify connectivity for validation and troubleshooting purposes:
- show ip route
- show ip arp
- show ip interface brief
- show interface status