Advanced Networking for Media Engineers¶
Info
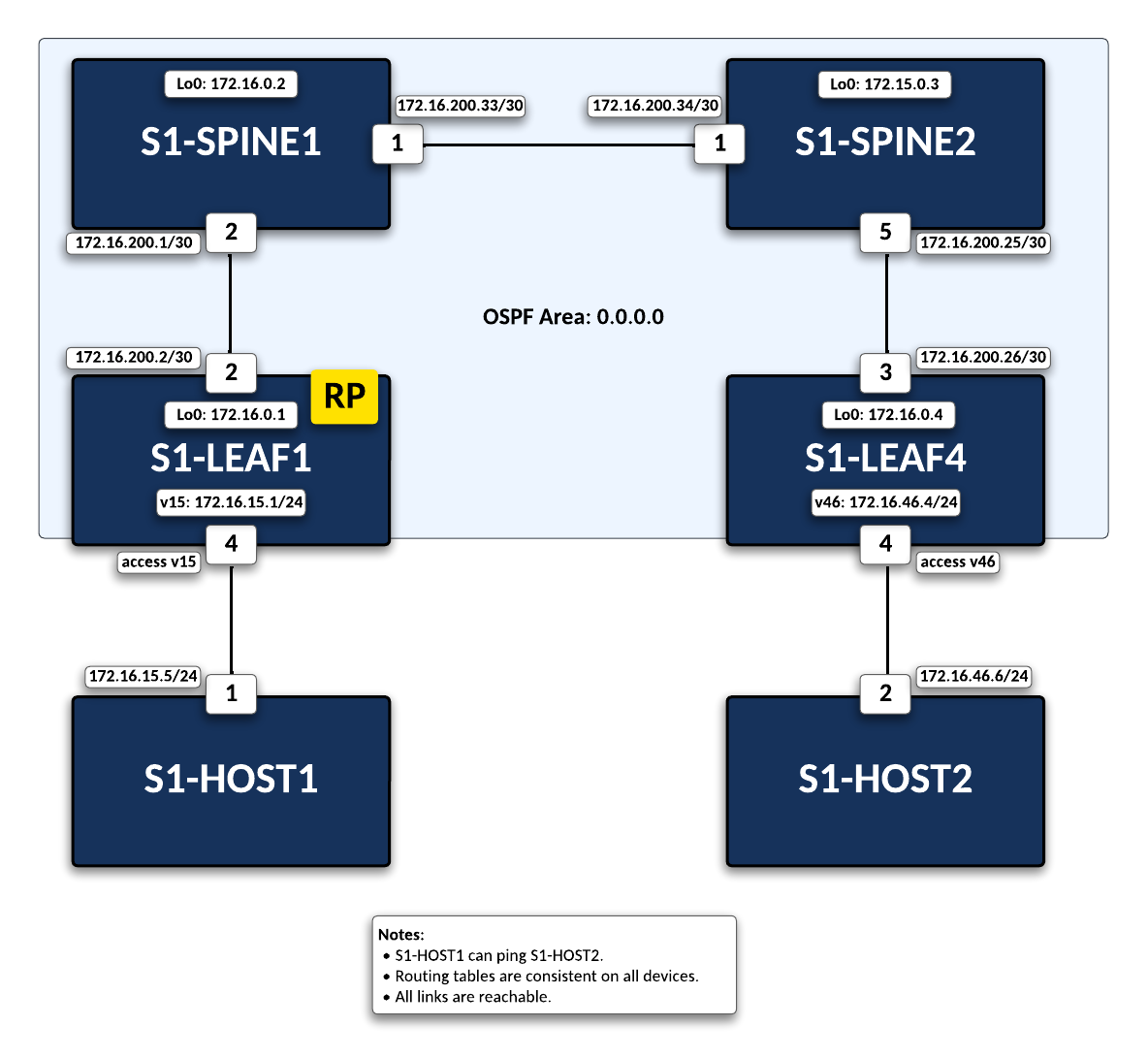
This lab is to understand the basics of a multicast topology. This lab will be a continuation of the concepts from the previous M & E Labs.
Info
This lab has been limited to the following devices: s1-Spine1, s1-Spine2, s1-Leaf1, s1-Leaf4, s1-Host1, and s1-Host2. Additional devices on this topology are out of scope for this lab.
Preparing The Lab¶
- Log into the LabAccess jumpserver:
- Type
labsat the Main Menu prompt. This will bring up additional lab menu selections. - Type
media-labsat this prompt to open the media lab section. - Type
media-mcastat this prompt and wait for the process to run. - The script will pre-configure the topology with the exception of s1-Leaf4, s1-Host1, and s1-Host2. The main task is to configure this device so there is connectivity between the two hosts.
- Type
Lab Tasks¶
Unlike the previous labs, this lab will have the configuration tasks as well as verification integrated together where you will test and verify as you work through the lab.
Configure and Verify the Network¶
-
Create vlan 46 and SVI for host access on
s1-Leaf4:Commands
Example
s1-leaf4(config)#vlan 46 s1-leaf4(config)#interface vlan 46 s1-leaf4(config-if-Vl46)#no autostate s1-leaf4(config-if-Vl46)#ip address 172.16.46.4/24Verify the layer 2 vlan has been created:
Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config)#show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports ----- -------------------------------- --------- ------------------------------- 1 default active Et6, Et7, Et8, Et9, Et10, Et11 Et12, Et13, Et14, Et15, Et16 Et17, Et18, Et19, Et20, Et21 Et22, Et23, Et24, Et25, Et26 Et27, Et28, Et29, Et30, Et31 Et32 12 VLAN0012 active 34 VLAN0034 active 46 VLAN0046 active CpuVerify the layer 3 VLAN SVI has been created:
Command
Expected Output
-
Enable connectivity for
s1-Host2ons1-Leaf4.On
s1-Leaf4, interface Ethernet4 is attached tos1-Host2. Configure the port as an access port in vlan 46:Commands
Example
Verification
Verify interface Eth4 is part of vlan 46:
Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et4)#show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports ----- -------------------------------- --------- ------------------------------- 1 default active Et6, Et7, Et8, Et9, Et10, Et11 Et12, Et13, Et14, Et15, Et16 Et17, Et18, Et19, Et20, Et21 Et22, Et23, Et24, Et25, Et26 Et27, Et28, Et29, Et30, Et31 Et32 12 VLAN0012 active 34 VLAN0034 active 46 VLAN0046 active Cpu, **Et4** -
Enable uplink connectivity to
s1-Spine2.On
s1-Leaf4, Ethernet3 is connected tos1-Spine2. Create a routed port for uplink access:Commands
Example
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et3)#interface ethernet 3 s1-leaf4(config-if-Et3)#no switchport s1-leaf4(config-if-Et3)#ip address 172.16.200.26/30 s1-leaf4(config-if-Et3)#mtu 9214 s1-leaf4(config-if-Et3)#no shutdownVerification
Verify interface Eth3 is configured as a routed port with the correct IP address:
Command
Expected Output
-
Configure OSPF and verify connectivity.
On
s1-Leaf4, create a loopback interface and assign an IP address to be used as the Router-ID. Then, enable OSPF with process ID 6500 and assign the networks to be advertised:Commands
interface Loopback0 ip address 172.16.0.4/32 ! router ospf 6500 router-id 172.16.0.4 passive-interface Loopback0 passive-interface Vlan46 network 172.16.0.0/24 area 0.0.0.0 network 172.16.46.0/24 area 0.0.0.0 network 172.16.200.24/30 area 0.0.0.0Example
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et3)#interface loopback 0 s1-leaf4(config-if-Lo0)#ip address 172.16.0.4/32 s1-leaf4(config-if-Lo0)# s1-leaf4(config-if-Lo0)#router ospf 6500 s1-leaf4(config-router-ospf)#router-id 172.16.0.4 s1-leaf4(config-router-ospf)#passive-interface loopback 0 s1-leaf4(config-router-ospf)#passive-interface vlan46 s1-leaf4(config-router-ospf)#network 172.16.0.0/24 area 0.0.0.0 s1-leaf4(config-router-ospf)#network 172.16.46.0/24 area 0.0.0.0 s1-leaf4(config-router-ospf)#network 172.16.200.24/30 area 0.0.0.0Verification
Verify the loopback0 interface has been configured with the correct IP address:
Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config-router-ospf)#show ip int br Interface IP Address Status Protocol MTU Ethernet3 172.16.200.26/30 up up 1500 Loopback0 172.16.0.4/32 up up 65535 Management0 192.168.0.17/24 down notpresent 1500 Vlan46 172.16.46.4/24 up up 1500Verify the OSPF neighbor adjacency is established with its neighbor,
s1-Leaf1:Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et3)#show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID VRF Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 172.16.0.3 default 1 FULL/DR 00:00:37 172.16.200.25 Ethernet3Verify routes are being learned via OSPF from
s1-Leaf1on interface Eth3:Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4#show ip route Gateway of last resort: S 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.0.254, Management0 O 172.16.0.1/32 [110/40] via 172.16.200.25, Ethernet3 O 172.16.0.2/32 [110/30] via 172.16.200.25, Ethernet3 O 172.16.0.3/32 [110/20] via 172.16.200.25, Ethernet3 C 172.16.0.4/32 is directly connected, Loopback0 O 172.16.15.0/24 [110/40] via 172.16.200.25, Ethernet3 C 172.16.46.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan46 O 172.16.200.0/30 [110/30] via 172.16.200.25, Ethernet3 C 172.16.200.24/30 is directly connected, Ethernet3 O 172.16.200.32/30 [110/20] via 172.16.200.25, Ethernet3 C 192.168.0.0/24 is directly connected, Management0 -
Test connectivity across network from
s1-Host2.Connect to
s1-Host2over SSH or from the console and test ICMP reachability tos1-Host1and its gateway.Test ICMP reachability to
s1-Host1gateway:Command
Test ICMP reachability to
s1-Host1:Command
-
Enable Multicast Routing.
On
s1-Leaf4we will be enabling multicast routing and assigning the interfaces to participate in multicast routing. Additionally, we will define the RP address on the switch.Commands
router multicast ipv4 software-forwarding sfe # (1) ! ip pim rp-address 172.16.0.1 ! interface Vlan46 ip pim sparse-mode ! ! interface Ethernet3 ip pim sparse-mode ! ip multicast-routing- In this lab environment, we will be leveraging the software based forwarding agent for multicast.
Example
s1-leaf4(config)#router multicast s1-leaf4(config-router-multicast)#ipv4 s1-leaf4(config-router-multicast-ipv4)#software-forwarding sfe s1-leaf4(config)#ip pim rp-address 172.16.0.1 s1-leaf4(config)#int vlan 46 s1-leaf4(config-if-Vl46)#ip pim sparse-mode s1-leaf4(config-if-Vl46)#int et3 s1-leaf4(config-if-Et3)#ip pim sparse-mode s1-leaf4(config)#ip multicast-routingVerification
Verify the RP is configured and up:
Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4(config-if-Et3)#sh ip pim rp Group: 224.0.0.0/4 RP: 172.16.0.1 Uptime: 0:02:56, Expires: never, Priority: 0, Override: FalseVerify there is a PIM neighbor on interface Ethernet3:
Command
Expected Output
-
Verify multicast operation between
s1-Host1ands1-Host2.-
Start the multicast server on
s1-Host1. You will do this by getting back into the CLI ofs1-Host1either through the console, or by clicking on it on the topology network diagram. You will then enter the following commands to drop down to text, and execute a shell script.Note
The shell script will run for 1800 seconds (30 min).
Commands
Expected Output
[arista@s1-host1 flash]$ Client connecting to 239.103.1.1, UDP port 5001 Sending 1470 byte datagrams Setting multicast TTL to 10 UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default) ------------------------------------------------------------ [ 3] local 10.33.157.26 port 38605 connected with 239.103.1.1 port 5001 ------------------------------------------------------------ Client connecting to 239.103.1.3, UDP port 5001 Sending 1470 byte datagrams Setting multicast TTL to 10 UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default) ------------------------------------------------------------ ------------------------------------------------------------ Client connecting to 239.103.1.2, UDP port 5001 Sending 1470 byte datagrams Setting multicast TTL to 10 UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default) ------------------------------------------------------------ [ 3] local 10.33.157.26 port 53682 connected with 239.103.1.2 port 5001 [ 3] local 10.33.157.26 port 40187 connected with 239.103.1.3 port 5001 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth [ 3] 0.0- 1.0 sec 31.6 KBytes 259 Kbits/sec Open a new ssh session leaving the source script running -
Start the multicast receiver on
s1-Host2. You will do this by getting back into the CLI ofs1-Host2either through the console, or by clicking on it on the topology network diagram. You will then enter the following commands to drop down to text, and execute a shell script.Commands
Expected Output
[arista@s1-host2 ~]$ ------------------------------------------------------------ Server listening on UDP port 5001 Binding to local address 239.103.1.1 Joining multicast group 239.103.1.1 Receiving 1470 byte datagrams UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default) ------------------------------------------------------------ ------------------------------------------------------------ Server listening on UDP port 5001 Binding to local address 239.103.1.2 Joining multicast group 239.103.1.2 Receiving 1470 byte datagrams UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default) ------------------------------------------------------------ -
Review the multicast routing table on
s1-Leaf1for the multicast source:Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf1#show ip mroute RPF route: U - From unicast routing table M - From multicast routing table 239.103.1.1 0.0.0.0, 0:01:56, RP 172.16.0.1, flags: W Incoming interface: Register Outgoing interface list: Ethernet2 172.16.15.5, 0:02:24, flags: SLN Incoming interface: Vlan15 RPF route: [U] 172.16.15.0/24 [0/1] Outgoing interface list: Ethernet2 239.103.1.2 0.0.0.0, 0:01:56, RP 172.16.0.1, flags: W Incoming interface: Register Outgoing interface list: Ethernet2 172.16.15.5, 0:02:24, flags: SLN Incoming interface: Vlan15 RPF route: [U] 172.16.15.0/24 [0/1] Outgoing interface list: Ethernet2 239.103.1.3 172.16.15.5, 0:02:24, flags: SLN Incoming interface: Vlan15 RPF route: [U] 172.16.15.0/24 [0/1] Outgoing interface list: Ethernet2 -
Review the multicast routing table on
s1-Leaf4for the multicast receiver:Command
Expected Output
s1-leaf4#show ip mroute RPF route: U - From unicast routing table M - From multicast routing table 239.103.1.1 0.0.0.0, 0:00:17, RP 172.16.0.1, flags: W Incoming interface: Ethernet3 RPF route: [U] 172.16.0.3/32 [110/40] via 172.16.200.25 Outgoing interface list: Vlan46 172.16.15.5, 0:00:13, flags: S Incoming interface: Ethernet3 RPF route: [U] 172.16.15.0/24 [110/40] via 172.16.200.25 Outgoing interface list: Vlan46 239.103.1.2 0.0.0.0, 0:00:17, RP 172.16.0.1, flags: W Incoming interface: Ethernet3 RPF route: [U] 172.16.0.3/32 [110/40] via 172.16.200.25 Outgoing interface list: Vlan46 172.16.15.5, 0:00:13, flags: S Incoming interface: Ethernet3 RPF route: [U] 172.16.15.0/24 [110/40] via 172.16.200.25 Outgoing interface list: Vlan46
-
Success
If your s1-Host2 showed it was receiving multicast data and your multicast routing table output reflected what was expected, you configured everything correctly!