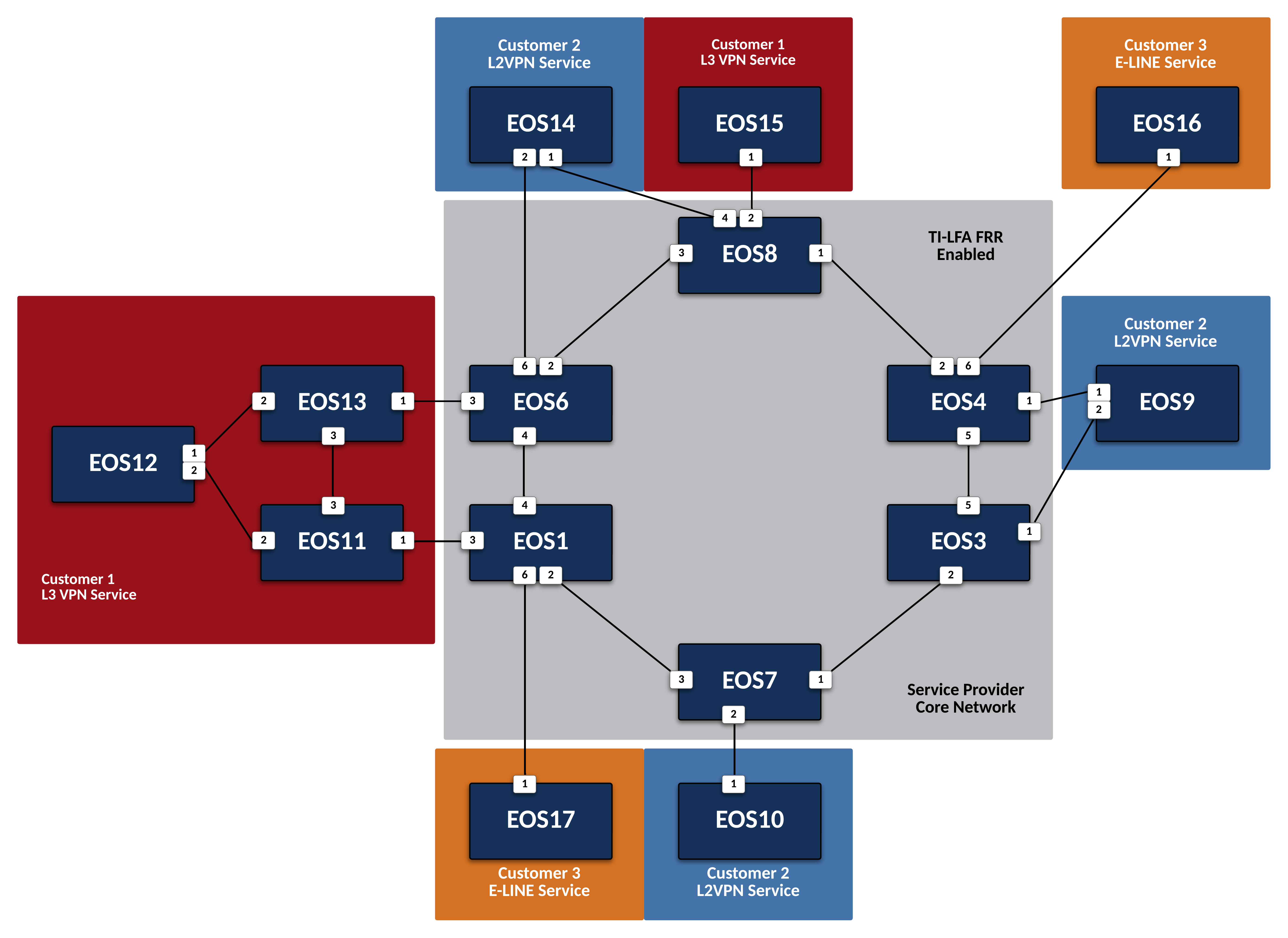
Enable TI-LFA Fast Reroute for ISIS-SR¶
Preparing The Lab¶
- Log into the LabAccess jumpserver:
- Type
labs, or select Option 97 to get to theAdditional Labsmenu. - Type or select the option for
ring-topology-evpn-supplemental-labsin order to get to the EVPN labs. - Type
tilfain this menu to configure the topology with the necessary prerequisites.
- Type
Lab Tasks¶
-
Enable Topology Independent Loop Free Alternate, or TI-LFA, calculation to occur on
EOS1.-
First, enable TI-LFA to protect against link failures in the Level-2 IS-IS topology.
Note
TI-LFA will calculate backup paths between the IS-IS enabled nodes assuming that the primary best path has failed. In the event of an actual failure, hardware forwarding would switch to this backup path in 50 ms. This would normally be paired with BFD monitoring. In the virtual ATD labs, it is not possible to simulate actual failures, but the TI-LFA control-plane can still be validated.
-
Set a delay so that traffic will transition to the post-failure path only after the network has fully converged.
Note
Normally, IS-IS would use the TI-LFA calculated path only until the local router has reconverged after the failure. To prevent micro-loops during failure events, we introduce a delay for the router to switch from the TI-LFA calculated backup path to give the network time to converge globally.
-
-
Repeat the above configuration steps on all other Service Provider nodes.
-
Configure
EOS3,EOS4, andEOS6-EOS8for TI-LFA calculation.
-
Testing¶
Verify local ISIS-SR TI-LFA status and forwarding on EOS1.
-
Display the Node SIDs of the topology and observe that some now have Protection.
Note
You will notice some prefix-segments are not protected. This is due to that fact that an ECMP route for those Nodes is already present, so there is no need to further calculate a backup path. If a link fails in the ECMP group, it will automatically use the other. Once a single link is the best path, it would then calculate a TI-LFA backup path. You can observe which nodes have an ECMP route with show ip route and verifying which prefixes have more than one next-hop listed.
-
Display the logic
EOS1uses to calculate the backup path to the other nodes in the topology.Abstract
The Constraint is how EOS displays what would happen in the event of a given failure; basically following the format “If Constraint is true, then use Path to reach Destination.”
-
Display primary and backup path information from
EOS1toEOS8.Note
We can check how
EOS1will reachEOS8by first looking up the SR tunnel for theEOS8node prefix 8.8.8.8/32. Then we can check the TI-LFA tunnel index, which in the below example happened to be 7 though this may vary in your lab. Lastly, we can verify that the MPLS hardware table has programmed the label corresponding to theEOS8Node-SID to use the TI-LFA Tunnel. -
Verify L2VPN routes towards
EOS7are using the TI-LFA tunnel fromEOS3.Note
We will trace the MAC of
EOS10, which in this example is 1426.0c23.74e4. You should replace this in the commands below with the MAC of Et1 onEOS10which can be found in the command show interface Ethernet1. Likewise the tunnel index of 3 should be replaced with the index found in parenthesis from the l2rib output.
Success
Lab Complete!