IS-IS Protocol Configuration - Class Guide¶
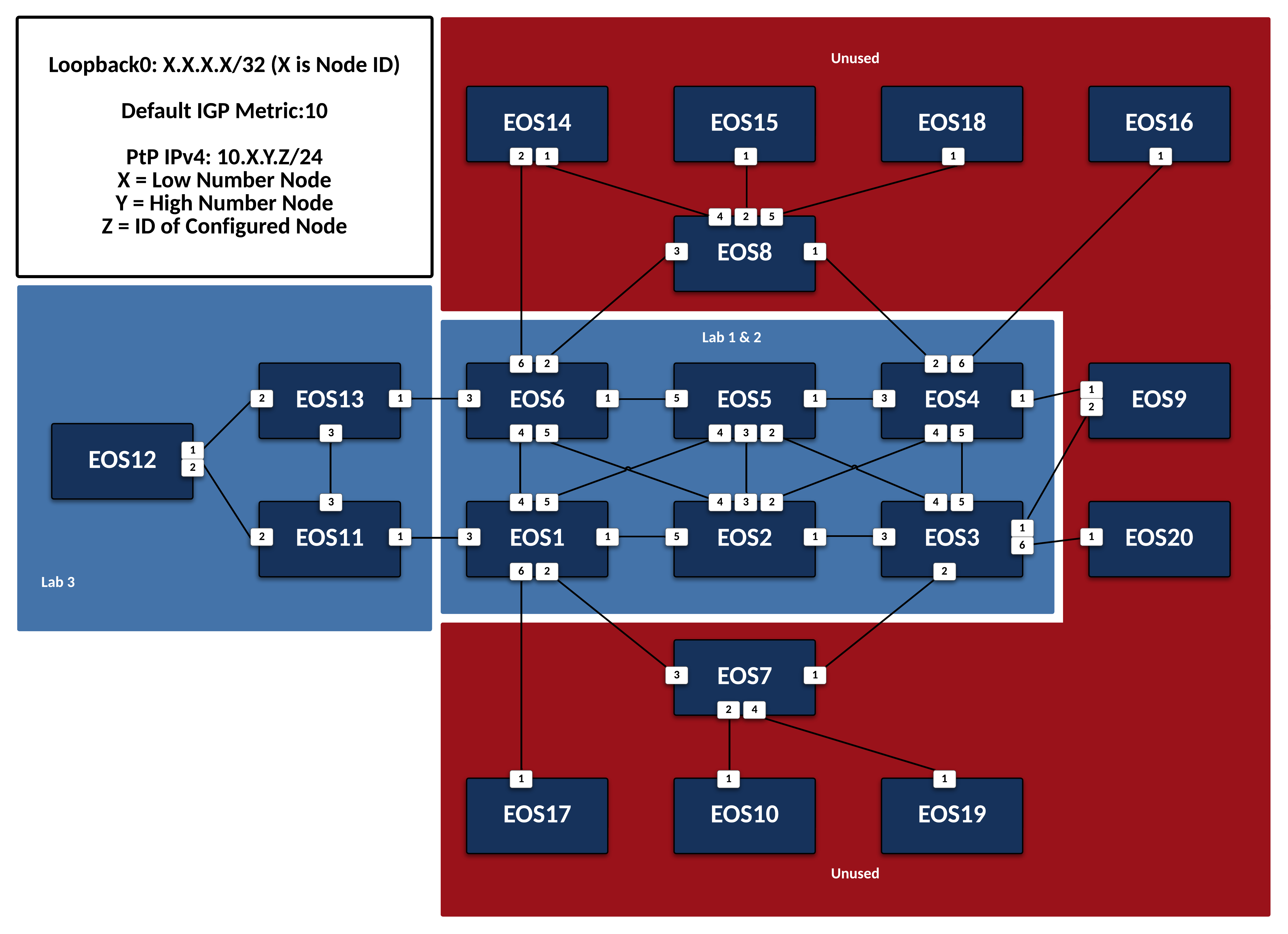
The following overall topology is used for the below labs.
IP Addressing
IP addressing is already configured for all labs.
Lab 1: Configure IS-IS as a Single Flood Domain¶
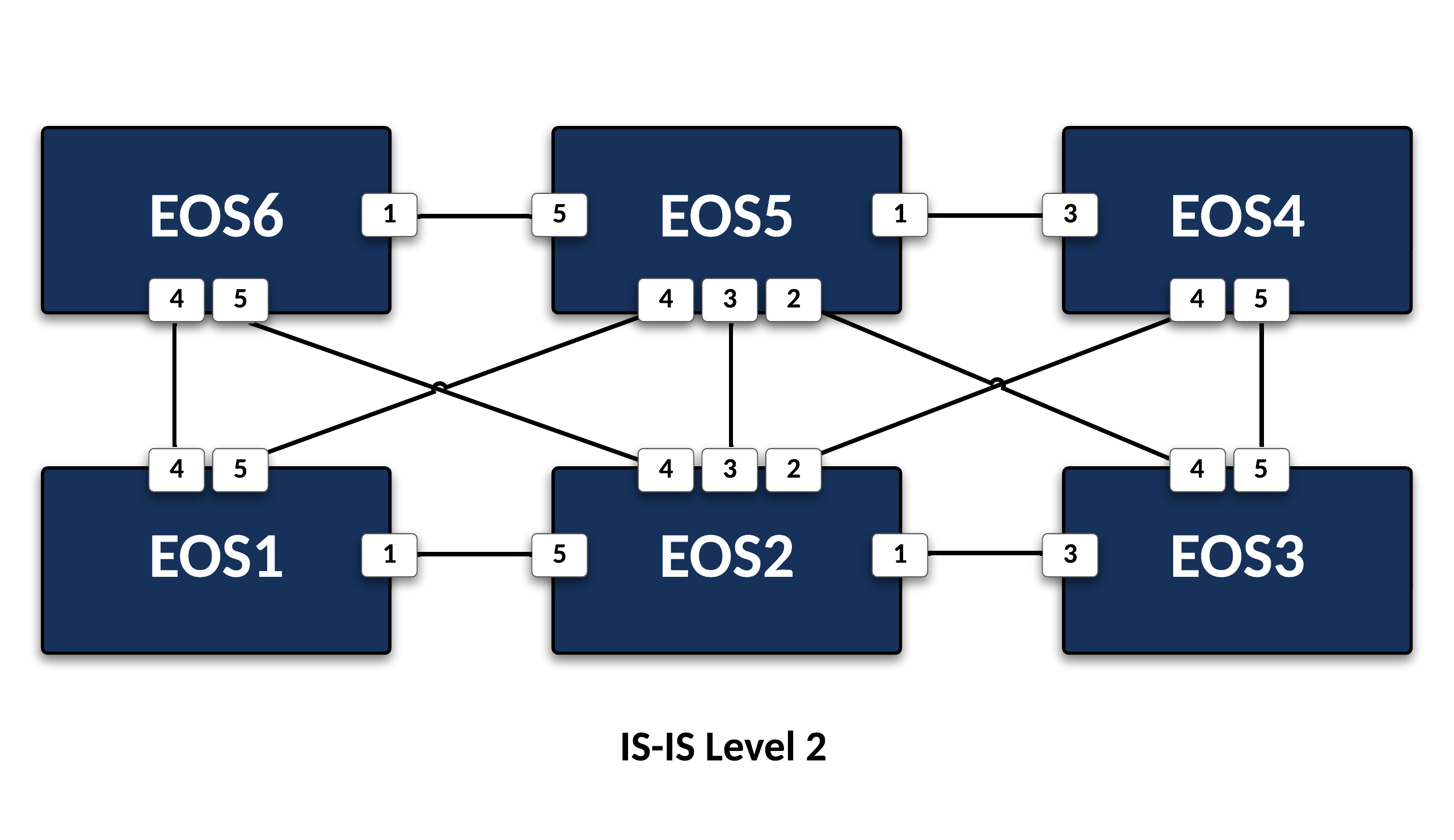
Lab 1 uses the following topology:
Preparing The Lab¶
- Log into the LabAccess jumpserver:
- Type
labsto get to theAdditional Labsmenu. - Type
isis-lab-guidein order to get to the ISIS Lab Guide labs. - Type
lab1in this menu in order to begin deploying configurations for this lab. - Wait until you are prompted that the lab deployment is complete. This will take some time.
- Type
Lab Tasks¶
-
Configure
EOS1toEOS6links to be in a single area and flood domain:- Enable ipv4 routing.
- Use area 0000.
- Use IS-IS Instance name of 1.
-
Match the system-id of each device to the name of the device. (1)
- Eg.
EOS1’slast system-id hextet will be 0001 andEOS6’swill be 0006
- Eg.
-
Advertise all loopbacks.
- Ensure there are no pseudonodes in the environment.
-
All intermediate systems should have all routes from other intermediate systems.
- All intermediate system loopbacks should be able to reach each other.
-
Look at the isis database details:
- Are there any pseudonodes? If so, why?
- Are there multiple link state databases? If so, why?
- Make note of reachability information. What types of reachability are being advertised?
-
Look at the routing table and make a note of what it looks like currently.
- How many routes are there in the
show ip route summary?
- How many routes are there in the
Lab 2: Loopback Only Advertisements in LSPs¶
Lab 2 uses the following topology:
Preparing The Lab¶
Note
If you are continuing from Lab 1, you can skip these steps and go directly to Lab Tasks.
- Log into the LabAccess jumpserver:
- Type
labsto get to theAdditional Labsmenu. - Type
isis-lab-guidein order to get to the ISIS Lab Guide labs. - Type
lab2in this menu in order to begin deploying configurations for this lab. - Wait until you are prompted that the lab deployment is complete. This will take some time.
- Type
Lab Tasks¶
-
Configure IS-IS on
EOS1toEOS6so that only loopback reachability is advertised in LSPs.- Route maps should not be used.
-
All intermediate systems should have only loopback routes from other intermediate systems.
- All intermediate system loopbacks should be able to reach each other.
-
Look at the IS-IS database details:
- Make note of reachability information. What types of reachability are being advertised?
- How did this change from the last section?
-
Look at the routing table and make a note of what it looks like currently:
- How many routes are there in the ‘show ip route summary?’
- How did the routing table change from the last section?
Lab 3: Broadcast Network¶
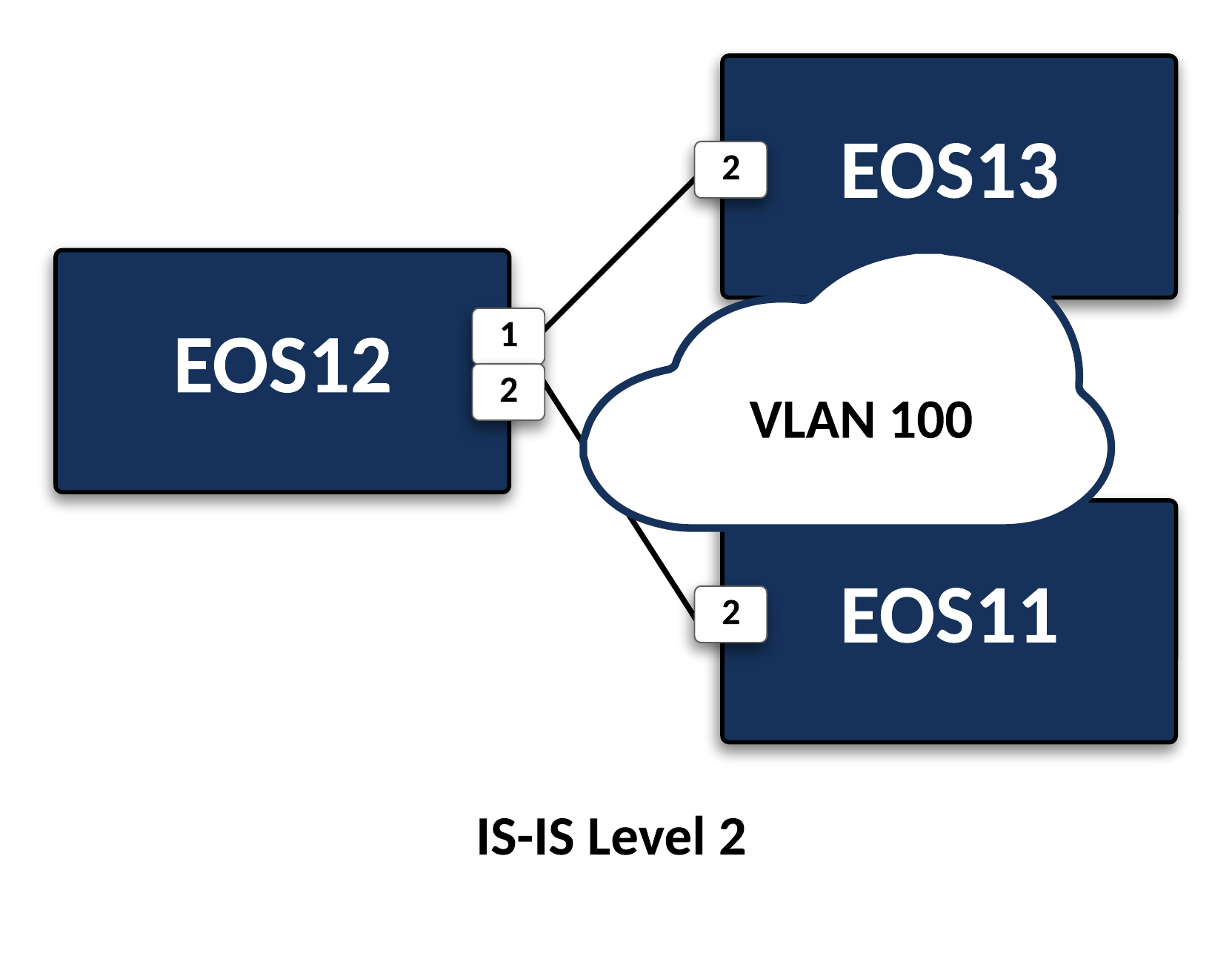
Lab 3 uses the following topology:
Preparing The Lab¶
Note
If you are continuing from Lab 2, you can skip these steps and go directly to Lab Tasks.
- Log into the LabAccess jumpserver:
- Type
labsto get to theAdditional Labsmenu. - Type
isis-lab-guidein order to get to the ISIS Lab Guide labs. - Type
lab3in this menu in order to begin deploying configurations for this lab. - Wait until you are prompted that the lab deployment is complete. This will take some time.
- Type
Lab Tasks¶
-
Configure IS-IS between
EOS11,EOS12, andEOS13using VLAN 100:- Enable ipv4 routing
- Use area 0000
- Use ISIS Instance name of 1
- Continue using a single flood domain
-
Match the system-id of each device to the name of the device (1)
- Eg.
EOS11’s last system-id hextet will be 0011 andEOS13’s will be 0013.
- Eg.
-
Advertise loopbacks into IS-IS.
- Only loopbacks should be advertised into the global routing table.
-
Look at IS-IS neighbors:
- How many adjacencies do you have per device?
-
Look at the IS-IS database:
- How does the IS-IS Database differ on the broadcast network?
- Are there any pseudonodes?
- If yes: How can you distinguish the pseudonode from other adjacencies?